Embark on a journey to explore the variances between corporate finance and business finance, delving into the intricacies that distinguish these two essential aspects of the financial world.
As we navigate through the nuances of each type of finance, we will uncover the fundamental disparities that shape their applications and impact on real-world scenarios.
Introduction to Corporate Finance and Business Finance
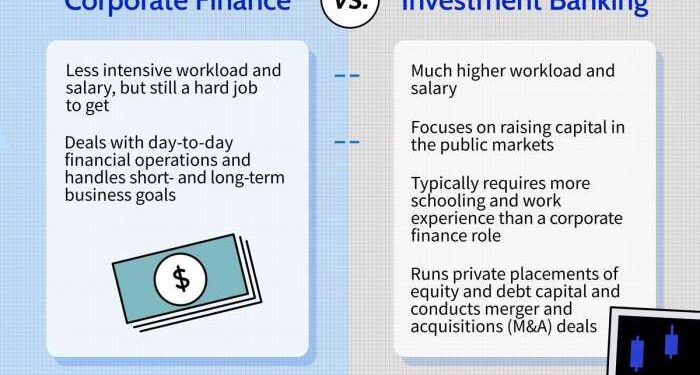
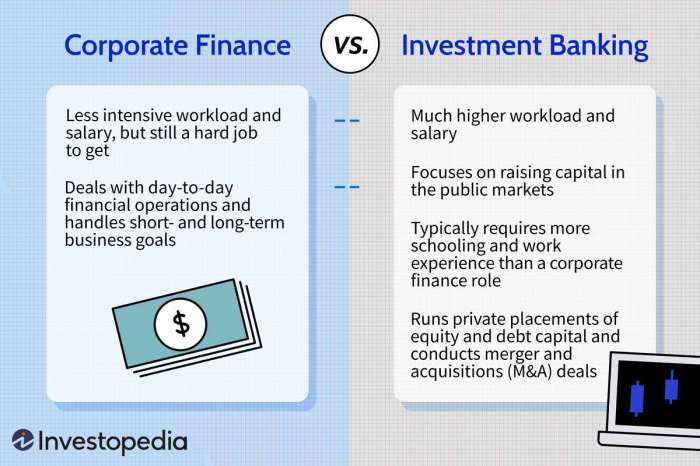
Corporate finance and business finance are two essential areas of finance that play a crucial role in the financial operations of companies. Corporate finance focuses on the financial decisions made within a corporation, such as capital investment, funding sources, and capital structure management.
On the other hand, business finance encompasses a broader scope, including financial management in a business setting, such as budgeting, financial planning, and financial analysis.The primary differences between corporate finance and business finance lie in their focus and scope. Corporate finance deals with strategic financial decisions within a corporation, while business finance covers a wider range of financial activities in a business context.
Examples of Corporate Finance and Business Finance in Real-World Scenarios
- Corporate Finance Example: One example of corporate finance in action is when a company decides to issue bonds to raise capital for a new project. The finance team would analyze the cost of debt and the impact on the company's overall financial health before making a decision.
- Business Finance Example: In a business finance context, a small business owner creating a budget for the upcoming year is a common example. The owner would consider factors like revenue projections, expenses, and cash flow to ensure the business's financial stability.
Scope and Focus of Corporate Finance
Corporate finance is a specialized area within finance that deals with the financial decisions made by corporations to maximize shareholder value and ensure the long-term sustainability of the business.
Areas of Focus within Corporate Finance
- Capital Budgeting: Involves making decisions regarding which investment projects to undertake to increase the value of the company.
- Capital Structure: Focuses on determining the mix of debt and equity financing that will optimize the company's cost of capital.
- Working Capital Management: Involves managing the company's short-term assets and liabilities to ensure smooth operations.
- Dividend Policy: Refers to decisions related to how profits are distributed to shareholders through dividends.
- Risk Management: Involves identifying and mitigating financial risks that could impact the company's financial performance.
Objectives and Goals of Corporate Finance
- Maximizing Shareholder Wealth: The primary goal of corporate finance is to increase the value of the company and in turn, maximize returns for shareholders.
- Optimizing Capital Structure: By finding the right balance between debt and equity financing, companies can reduce their cost of capital and enhance profitability.
- Ensuring Financial Stability: Corporate finance aims to ensure the financial stability of the company by managing risks effectively and maintaining adequate liquidity.
Key Financial Decisions in Corporate Finance
- Investment Decisions: Determining where to allocate financial resources to generate the highest returns.
- Financing Decisions: Choosing the right mix of debt and equity to fund operations and growth.
- Dividend Decisions: Deciding how much profit to distribute to shareholders and how much to retain for reinvestment.
- Risk Management Decisions: Identifying and addressing potential risks that could impact the financial health of the company.
Scope and Focus of Business Finance

Business finance encompasses various financial activities within an organization to manage funds effectively for achieving business goals and objectives. This includes making financial decisions, analyzing financial data, and planning for the future financial needs of the business.
Key Components of Business Finance
- Financial Planning: Involves setting financial goals, creating budgets, and forecasting future financial performance.
- Financial Analysis: Examining financial data to assess the financial health of the business and make informed decisions.
- Investment Decisions: Evaluating potential investments to determine their profitability and impact on the business.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating financial risks to protect the business from potential losses.
Goals and Objectives of Business Finance
- Maximizing Profitability: Increasing revenue and minimizing expenses to enhance the financial performance of the business.
- Ensuring Liquidity: Maintaining sufficient cash flow to meet short-term financial obligations and cover operational expenses.
- Managing Growth: Funding expansion opportunities and strategic initiatives to support business growth and development.
Financial Strategies in Business Finance
- Debt Financing: Borrowing money from external sources to fund business operations or investments.
- Equity Financing: Selling ownership stakes in the business to raise capital for growth and expansion.
- Working Capital Management: Efficiently managing current assets and liabilities to ensure smooth operations and cash flow.
Financial Management in Corporate vs. Business Finance
Financial management practices in corporate finance and business finance have similarities and differences that stem from the scale and structure of the organizations involved. In corporate finance, the focus is on maximizing shareholder value through strategic financial decision-making, while business finance tends to concentrate on managing finances to ensure the sustainability and growth of the business.
Financial Risk Management
In corporate finance, financial risk is managed through a combination of diversification, hedging strategies, and financial instruments such as derivatives. The goal is to mitigate risks that could impact the company's financial performance and shareholder value. On the other hand, in business finance, risk management is often more conservative, with a focus on cash flow management, debt reduction, and maintaining liquidity to weather economic uncertainties.
Financial Performance Measurement
In corporate finance, financial performance is measured using metrics such as return on investment (ROI), earnings per share (EPS), and market value added (MVA). These indicators help assess the effectiveness of financial strategies in creating value for shareholders. In contrast, business finance evaluates financial performance through metrics like cash flow analysis, profit margins, and return on assets (ROA).
The emphasis is on operational efficiency and profitability to sustain business operations and growth.
Investment Decisions in Corporate and Business Finance
Investment decisions play a crucial role in both corporate finance and business finance, guiding the allocation of resources to maximize returns. However, the approach and factors considered in making these decisions can differ significantly between the two.
Approach to Investment Decisions in Corporate Finance
In corporate finance, investment decisions are typically made with a focus on maximizing shareholder wealth. This involves evaluating potential projects or investments based on their expected returns and risks. Corporate finance professionals often use financial models such as Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR) to assess the profitability of investments and make informed decisions on capital allocation.
Factors Considered in Investment Decisions in Business Finance
In business finance, investment decisions are influenced by various factors, including the company's financial goals, industry trends, market conditions, and regulatory environment. Business finance managers often consider the company's liquidity position, cash flow projections, and risk tolerance when evaluating investment opportunities.
They also assess the impact of investments on the overall business strategy and long-term sustainability of the company.
Unique Investment Strategies in Corporate and Business Finance
- Corporate finance often involves strategic investments in mergers and acquisitions, capital projects, and research and development initiatives to drive growth and enhance competitive advantage.
- Business finance, on the other hand, may focus on short-term investments in working capital management, inventory optimization, and cost-saving measures to improve operational efficiency and profitability.
Summary
In conclusion, the comparison between corporate finance and business finance unveils a realm of distinct practices and strategies that cater to the unique needs of organizations. By understanding these differences, we gain valuable insights into the financial landscape that drives businesses forward.
FAQ Section
What is the main difference between corporate finance and business finance?
Corporate finance focuses on managing the capital structure of corporations, while business finance deals with financial decisions in a broader sense, including small businesses and entrepreneurial ventures.
How does financial management differ in corporate and business finance?
Financial management in corporate finance involves optimizing capital structure and maximizing shareholder value, whereas in business finance, it focuses on day-to-day financial operations and cash flow management.
What are some unique investment strategies in corporate finance compared to business finance?
Corporate finance often involves complex investment decisions relating to mergers, acquisitions, and capital budgeting, whereas business finance may focus more on short-term investments and operational expenses.